Configuring OSPF Interface Cost
Changing OSPF interface cost is a simple and easy way to manipulate the OSPF routes in the routing table. This lab will discuss and demonstrate the configuration and verification of OSPF Interface Cost.
Real World Application & Core Knowledge
Unlike the metric in RIP which is determined by hop count and EIGRP’s crazy mathematical formulated metric, OSPF is a little more simple. The default formula to calculate the cost for the OSPF metric is (10^8/BW).
By default the metrics reference cost is 100Mbps, so any link that is 100Mbps will have a metric of 1. a T1 interface will have a metric of 64 so in this case if a router is trying to get to a FastEthernet network on a router that is through a T1 the metric would be 65 (64 +1).
You do however have the ability to statically specify a metric on a per interface basis by using the ip ospf cost # where the cost is an integer between 1-65535.
So the big question is why would you want to statically configure a metric?
The biggest advantage of statically configuring an OSPF metric on an interface is to manipulate which route will be chosen dynamically via OSPF. In a nut shell its like statically configuring a dynamic protocol to use a specific route. Pretty cool huh?
In this lab you’ll increase the interface cost on R5’s FastEthernet0/0 interface to make R4 the preferred route on R1 to get to the 10.90.145.0/24 network.
Familiarize yourself with the following new command(s);
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ip ospf cost # | This command is executed in interface configuration mode to statically configure the OSPF interface cost of the specified interface. |
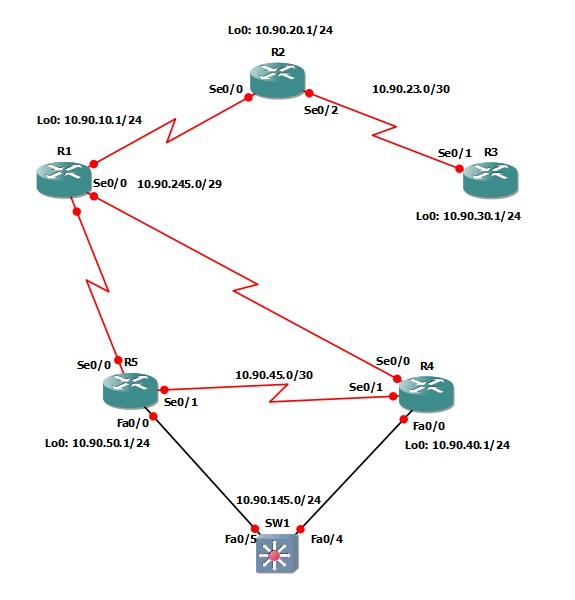
The following logical topology shown below is used in labs found through out Section 9 – Configuring OSPF;
Lab Prerequisites
- If you are using GNS3 than load the Free CCNA Workbook GNS3 topology than start devices; R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and SW1.
- Establish a console session with devices R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and SW1 than load the initial configurations provided below by copying the config from the textbox and pasting it into the respected routers console.
Lab Objectives
- Observe the routing table on R1, The route to 10.90.145.0/24 should be load balanced via R4 and R5.
- Configure R5’s 10.90.145.0/24 interface with the OSPF cost 100; afterwards verify R1’s routing table to see if R1 is using the R4 to get to the 10.90.145.0/24 route.
Lab Instruction
Objective 1. – Observe the routing table on R1, The route to 10.90.145.0/24 should be load balanced via R4 and R5.
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 4 masks
O IA 10.90.50.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.5, 02:09:40, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.40.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.4, 02:09:40, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.23.0/30 [110/128] via 10.90.245.2, 02:01:57, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.30.1/32 [110/129] via 10.90.245.2, 00:47:17, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.145.0/24 [110/65] via 10.90.245.5, 02:09:40, Serial0/0
[110/65] via 10.90.245.4, 00:11:37, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.45.0/30 [110/128] via 10.90.245.5, 02:09:40, Serial0/0
[110/128] via 10.90.245.4, 02:09:40, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.20.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.2, 02:01:57, Serial0/0
C 10.90.10.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.90.245.0/29 is directly connected, Serial0/0
R1#
Objective 2. – Configure R5’s 10.90.145.0/24 interface with the OSPF cost 100; afterwards verify R1’s routing table to see if R1 is using the R4 to get to the 10.90.145.0/24 route.
In order to make R4 the preferred route on R1, you must increase R5’s cost to the 10.90.145.0/24 network as both routers cost to the 10.90.145.0/24 network is 1 since 100Mbps is the default reference bandwidth of OSPF.
R5#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R5(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0 R5(config-if)#ip ospf cost 100 R5(config-if)#end R5# %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console R5#
After the cost has been changed on R5 verify that R1 is now using R4 as the next hop to get to the 10.90.145.0/24 network as shown below;
R1#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 9 subnets, 4 masks
O IA 10.90.50.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.5, 02:14:01, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.40.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.4, 02:14:01, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.23.0/30 [110/128] via 10.90.245.2, 02:06:18, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.30.1/32 [110/129] via 10.90.245.2, 00:51:38, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.145.0/24 [110/65] via 10.90.245.4, 00:15:59, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.45.0/30 [110/128] via 10.90.245.5, 02:14:01, Serial0/0
[110/128] via 10.90.245.4, 02:14:01, Serial0/0
O IA 10.90.20.1/32 [110/65] via 10.90.245.2, 02:06:18, Serial0/0
C 10.90.10.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
C 10.90.245.0/29 is directly connected, Serial0/0
R1#
