Configuring Static Route Redistribution
A Common way to get routes into routing protocols is through static route redistribution. This lab will discuss and demonstrate the configuration and verification of static route redistribution.
Real World Application & Core Knowledge
The most common way to advertise a default route into a routing protocol is via static distribution. What this does is that the router will take the static routes and translate them into the dynamic routing protocol so that way they can be advertised to neighbors whereas static routes by themselves are locally significant only.
When advertising a default route via static redistribution you have the ability to dynamically control something that is static. Also keep in mind you can control which default routes to advertise via a floating static route which would be useful when advertising a default route to a router which has internet connectivity.
When redistributing static routes you have the ability to manipulate which static routes you want to redistribute into a dynamic routing protocol using what is called a route-map. Static redistribution is the same process for any dynamic routing protocol and all dynamic routing protocols rather it be RIP, EIGRP or OSPF, all use the same commands to redistribute the static routes into the routing process.
To configure static redistribution you’ll use the redistribute static metric metric# whereas the metric is a statically configured metric which is assigned to the redistributed route(s). Keep in mind each dynamic routing protocol has a different type of metric. RIP uses hop counts, EIGRP uses K Values (bandwidth, load, delay, reliability and mtu), OSPF uses a cost based metric. With this in mind, the configuration for static route redistribution into a dynamic routing protocol will be different based on the routing protocol you’re redistributing into.
In this lab you will configure a static default route on R1 and redistribute that route into RIP.
Familiarize yourself with the following new command(s);
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| redistribute static metric metric# | This command is executed in router configuration mode rather it be RIP, EIGRP or OSPF to redistribute local static routes into the dynamic routing process to be dynamically advertised. The metric is configured differently on a per routing protocol basis. |
The following logical topology shown below is used in this lab;
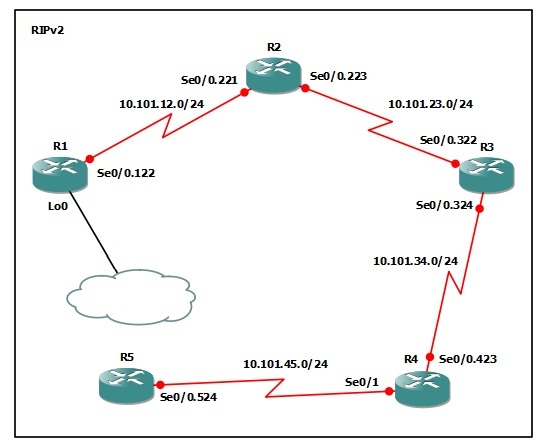
Lab Prerequisites
- If you are using GNS3 than load the Free CCNA Workbook GNS3 topology than start devices; R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5
- Establish a console session with devices R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 than load the initial configurations provided below by copying the config from the textbox and pasting it into the respected routers console.
Lab Objectives
- Create a loopback interface on R1 using the IP address of 172.29.41.1/24
- Create a default static route on R1 pointing to 172.29.41.5
- Redistribute all static routes into the RIP routing process using a metric of 5
- Verify that the static default route being redistributed is properly propagated to R5.
Lab Instruction
Objective 1. – Create a loopback interface on R1 using the IP address of 172.29.41.1/24
R1#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)#interface loopback0 R1(config-if)# *Jul 15 18:56:30.351: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up R1(config-if)#ip add 172.29.41.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#
Objective 2. – Create a default static route on R1 pointing to 172.29.41.5
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.29.41.5
Objective 3. – Redistribute all static routes into the RIP routing process using a metric of 5
R1(config)#router rip R1(config-router)#redistribute static metric 5
Objective 4. – Verify that the static default route being redistributed is properly propagated to R5.
R5#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is 10.101.45.1 to network 0.0.0.0
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 4 subnets
R 10.101.12.0 [120/3] via 10.101.45.1, 00:00:22, Serial0/0.524
R 10.101.23.0 [120/2] via 10.101.45.1, 00:00:22, Serial0/0.524
C 10.101.45.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0.524
R 10.101.34.0 [120/1] via 10.101.45.1, 00:00:22, Serial0/0.524
R* 0.0.0.0/0 [120/8] via 10.101.45.1, 00:00:01, Serial0/0.524
R5#
As shown above you can see that a default route is now present in the routing table on R5 learned via RIP.
